In the complex journey of parenthood, the path isn’t always straightforward. One twist is ectopic pregnancy, a situation where fertilized eggs implant outside the uterus, usually in the fallopian tubes. This reproductive problem can be challenging, but with knowledge and proactive steps, you can prevent it.
What is Ectopic Pregnancy
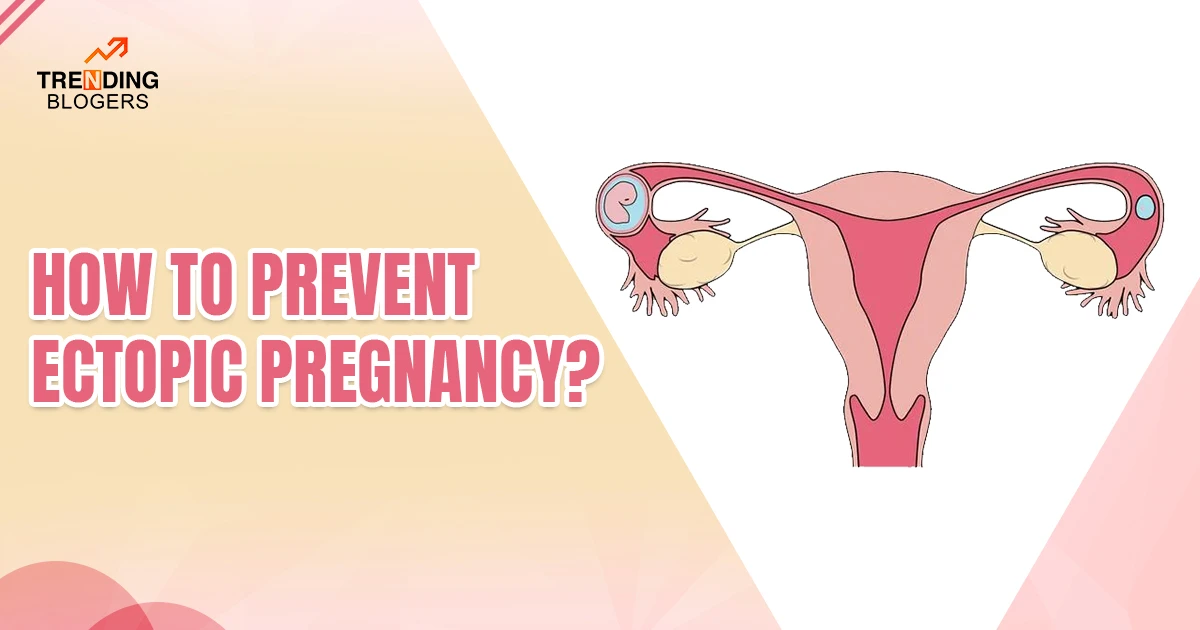
Ectopic Pregnancy is also Known as extrauterine pregnancy. It is a medical condition in which the fertilized egg develops outside the uterus, in areas including ovaries, the lower part of the cervix, or the belly, and mainly in the fallopian tube.
In approximately more than 90% of cases, the fertilized egg implants itself into a fallopian tube, known as “Tubal Pregnancy.” Tubal Pregnancy can be very dangerous as the fallopian tubes can break if they get stretched too much by the growing pregnancy and lead to a ruptured ectopic pregnancy.
According to the American Pregnancy Association, an alarming 1 in 50 pregnancies is ectopic, making it a critical concern for reproductive health. While the overall incidence might seem low, the potential complications are serious and warrant attention. The World Health Organization (WHO) reports that ectopic pregnancies are a leading cause of maternal morbidity and mortality during the first trimester. These figures emphasize the urgency of spreading awareness and implementing preventive measures.
Tips to Prevent Ectopic Pregnancy
- Early and Regular Check-ups: Early detection of pregnancies, combined with routine monitoring, can significantly reduce the risk of ectopic pregnancies. Immediate medical attention ensures that any deviation from the norm is addressed at earliest.
- Know Your Body: Every woman’s body is unique, and being aware of its signals is crucial. Pay attention to any abnormal symptoms, such as sharp pelvic pain, abnormal bleeding, or shoulder pain. Early recognition of these signs can facilitate timely intervention, preventing complications associated with ectopic pregnancies.
- Treat and Prevent STIs: Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) can increase the risk of ectopic pregnancies. Regular screenings and safe practices can help prevent STIs and minimize their impact on reproductive health. Open communication with your partner and practicing safe sex are important for a healthy sexual relationship.
- Address Past Reproductive Issues: If you have a history of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), endometriosis, or previous ectopic pregnancies, it’s important to discuss these with your healthcare provider. Understanding your medical history allows for proactive measures and personalized strategies to reduce the risk of recurrence.
- Fertility Treatments and Monitoring: Fertility treatments increase the risk of ectopic pregnancies and careful monitoring and supervision by fertility specialists can help minimize this risk.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Last but not least, a healthy lifestyle is the key to healthy pregnancy. Maintain a balanced diet, do regular exercise, and avoid harmful substances such as tobacco and excessive alcohol.
Symptoms of Ectopic Pregnancy:
The early ectopic pregnancy signs can be very similar to normal pregnancy symptoms. However, some additional symptoms are there that you might experience, including:
- Weakness or dizziness
- Vaginal bleeding
- Pain in the lower abdomen, lower back, and pelvis.
- Pain on one side of the body
- Discomfort during excretion
Causes of Ectopic Pregnancy:
Anything blocking the safe passage of a fertilized egg through the fallopian tube increases the possibility that the egg will implant in the tube. Some ectopic pregnancy causes are:
- Prior surgery in the abdomen or pelvis
- A prior ectopic pregnancy
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
- STD or a sexually transmitted infection
- Has a history of smoking cigarettes
- Pregnancy occurred with an intrauterine device (IUD) in place
- Endometriosis
- History of fertility treatment like in vitro fertilization (IVF)
- Pregnancy after the age of 35 years
How is an Ectopic Pregnancy Diagnosed?
Many people don’t realize that their pregnancy is ectopic until they visit their doctor for an ultrasound or prenatal appointment. In case you are experiencing signs like vaginal bleeding, stomach pain and discomfort in excretion during your pregnancy, you must consult a doctor. If your doctor suspects ectopic pregnancy, they will prescribe you tests like Blood Tests, Urine Test and Ultrasound.
How is an Ectopic Pregnancy Treated?
In some of the cases, spontaneous miscarriages can happen. However, if this is not happening, an ectopic pregnancy can be treated with the below-mentioned ways:
- Laparoscopic Procedures: Salpingectomy and salpingostomy are two laparoscopic surgeries that are used to treat ectopic pregnancies. In this method, a tiny incision is made near the navel or in the abdomen. Then, your doctor will use a thin tube with a laparoscope and camera lens to view the tubal area.
- Medication: An early ectopic is mostly treated with a medicine called methotrexate. It helps to dissolve the existing cells and stops the growth of cells. After this, the doctor will order another HCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) test to know how well the treatment works and whether you need medications.
- Emergency Surgery: If experiencing heavy bleeding, you may need emergency surgery through laparotomy (abdominal incision) or laparoscopically.
Bottom Line
Ectopic pregnancies may be challenging, but with awareness, knowledge, and a commitment to reproductive health, we can equip ourselves with preventive measures and immediate action. By taking proactive steps, such as early and regular check-ups, contraception choices, and addressing reproductive issues, individuals can have healthy pregnancy.
FAQs
Vaginal bleeding, pain in one side of your body, and bowel problems are some of the signs of ectopic pregnancy.
It is possible to have a baby after an ectopic pregnancy, even if you have lost one of the fallopian tubes.
Also Read About: What are the treatments for Infertility?